The text explores the significance of the hearth in human evolution, linking it to cooking, energy consumption, and social structure. The control of fire allowed early humans to cook food, improving energy yield and enabling larger brains and smaller guts. Archaeological evidence shows that fire usage became commonplace about 300,000 to 400,000 years ago, shaping daily life and social interactions around central hearths. It argues that the hearth served as a proto-altar, merging practical and ritualistic elements, fostering community through shared meals and storytelling, and reinforcing a sense of sacred space. Ultimately, the hearth transformed not just sustenance but the very essence of humanity.
Tag Archives: #Archaeology
Whispers on Stone: Why Paleolithic Rock Art Still Speaks to Us Today
The author plans to move to Portugal’s Côa Valley to deeply engage with Paleolithic rock art, viewing it as a living expression of human connection and cognition. This journey is about listening to ancient voices and understanding their significance, drawn from a personal and academic commitment to anthropology and human history through modern technologies.
The Echo of a Hand Across Millennia: Decoding the Cave Hand Stencil
Hand stencils, created by ancient humans using natural pigments, represent some of the earliest expressions of identity and belonging. These artworks, found in various locations worldwide, highlight the cognitive sophistication of early societies and reflect complex social structures. Evidence suggests that women and children actively participated in creating these stencils, emphasizing cultural transmission and inclusivity. The presence of deliberate details, like missing fingers, indicates a deeper symbolic significance often linked to spirituality. Discoveries of Neanderthal-made stencils challenge previous perceptions of these early humans, showcasing their creative capabilities. Ultimately, handprints serve as a timeless connection to our shared humanity and urge reflection on our desire for recognition and permanence.
Rock Art on Screen: 12 Free Documentaries That Bring the Painted Past to Life
By Seth Chagi for World of Paleoanthropology “We carry the torch of ancient storytellers each time we switch on a screen.” — Stoic reflection after too many late‑night documentary binges Rock art feels simultaneously intimate and cosmic—handprints that whisper I was here across 30,000 years. The internet, bless its algorithmic heart, is brimming with free filmsContinue reading “Rock Art on Screen: 12 Free Documentaries That Bring the Painted Past to Life”
A Touch Across Time: The Neanderthal Fingerprint That Changed Everything
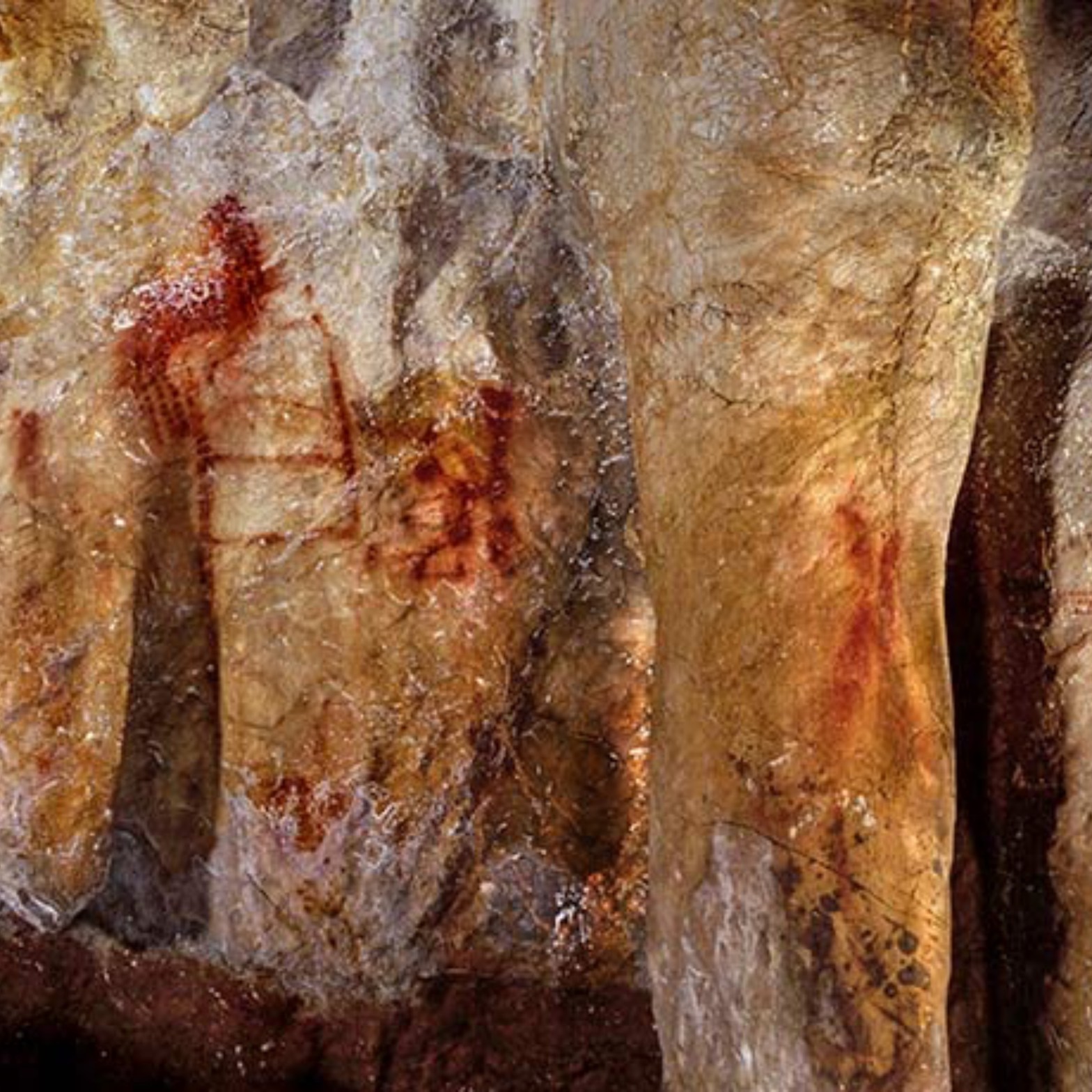
Archaeologists in San Lázaro, Spain, discovered a 43,000-year-old Neanderthal fingerprint, challenging perceptions of their cognitive abilities. The red ocher mark suggests intentionality and symbolic thought, previously attributed only to modern humans. This find promotes a reevaluation of Neanderthal culture, revealing their potential for complex cognition and creative expression.
What Did Neanderthals Think About Before Bed?
Imagine a world that looks nothing like the one we know today. It’s a place where surviving the day isn’t a metaphor—it’s a real struggle. When the sun goes down, it gets truly dark, much darker than anything we’re used to. As night falls, your priorities change. You’re not thinking about homework, crushes, or weekendContinue reading “What Did Neanderthals Think About Before Bed?”
The Lost Canvas of Humanity: What the World Would Look Like If Paleolithic Rock Art Survived
The Paleolithic era likely featured abundant rock art beyond caves, illustrating early human creativity and communication. Unfortunately, much of this open-air artwork has been lost due to weathering and erosion. Remaining sites, like those in the Coa Valley, reveal a glimpse of what once existed, suggesting a vibrant, artistic society. If more had survived, our understanding of prehistoric people would be richer, showcasing art as a vital part of daily life. This loss highlights the transient nature of human expression and its enduring significance despite impermanence.
Beyond the Grave: Burial and the Human Condition in Deep Time
In the remote depths of caves from Iraq to Spain and South Africa, our ancient relatives confronted the mystery of death—and in doing so, revealed the first stirrings of what it means to be human. From Neanderthals laying flowers beside their dead in Shanidar Cave, to the “Pit of Bones” at Sima de los Huesos, to the enigmatic chamber of Homo naledi in Rising Star Cave, early burial practices speak volumes about empathy, symbolism, and social bonds in deep time. Join us as we explore how these funerary rituals illuminate the origins of memory, grief, and the human soul.
Exploring Human Expression: The Origins of Art and Symbolism
The origins of art showcase human creativity’s deep evolutionary roots, extending beyond Homo sapiens to include Neanderthals and earlier hominins. Discoveries reveal symbolic expression dates back over 500,000 years, suggesting complex cognitive abilities and the importance of art for communication, spirituality, and social cohesion in ancient societies. Creativity connects us to our ancestors.
New Evidence for Ritualistic Burial by Homo Naledi
The journey of Homo naledi began with its discovery in the Rising Star Cave system, where these ancient remains have sparked debates about their significance in human evolution. Over time, new findings have added layers to our understanding, with the latest research proposing that Homo naledi may have engaged in purposeful burial practices. This challenges previous notions about cognitive abilities and cultural behaviors in early hominins, opening new avenues for exploration in the field of paleoanthropology.